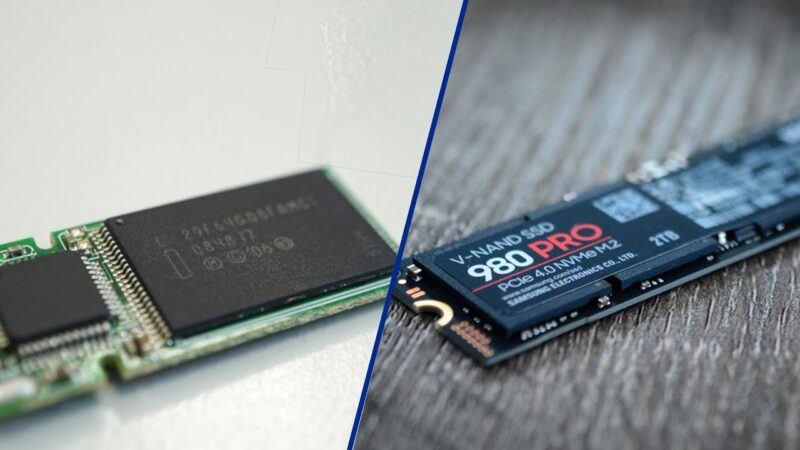
When it comes to data storage, the comparison between eMMC and SSD is akin to a debate between convenience and performance.
Both technologies have carved niches in the digital world, offering unique advantages that cater to different user needs.
Having knowledge about the nuances between eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) and SSD (Solid State Drive) is crucial for anyone looking to make an informed decision on storage solutions.
Today, I will talk about the characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks of each, aiming to shed light on which is the better choice for various applications.
Key Takeaways
- SSDs offer significantly higher performance and storage capacities than eMMC, making them better suited for demanding tasks and applications.
- eMMC provides a cost-effective storage solution, ideal for entry-level devices where high performance is not a priority.
- Durability and data integrity are stronger in SSDs due to advanced technologies like wear leveling and garbage collection.
- Upgrading from eMMC to SSD can be challenging or impossible for most devices, as eMMC is usually soldered onto the motherboard.
- While SSDs may use slightly more power than eMMC, they enhance overall efficiency and can contribute to improved battery life in devices.
The Basics
Before we start with the specifics, it’s important to establish a foundational understanding of what eMMC and SSDs represent in the storage world.
What is eMMC?

eMMC stands for embedded MultiMediaCard.
It’s a type of NAND flash memory, which means it’s a non-volatile storage medium that doesn’t require power to retain data.
eMMC is often soldered directly onto the motherboard of devices, making it a compact and cost-effective storage solution.
Commonly found in smartphones, tablets, and budget laptops, eMMC storage is known for its small physical footprint and affordability.
However, it typically offers less storage capacity (ranging from 32GB to 128GB) and slower transfer speeds compared to its Solid State Drive counterparts.
What is an SSD?

An SSD, or Solid State Drive, elevates the performance of data storage to new heights.
Unlike eMMC, SSDs do not have moving parts and offer superior read-and-write speeds, lower power consumption, and greater durability against physical impacts.
Solid State Drive technology varies, with connections via SATA (Serial ATA), mSATA, SATA Express, or PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interfaces, allowing for a wide range of applications from consumer electronics to enterprise data centers.
SSDs are renowned for their fast transfer speeds, with NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) protocols reaching up to 7.0GB/s and offering larger storage capacities, starting at 128GB and extending up to several terabytes.
Performance
When it comes to performance, SSDs unquestionably take the lead. The difference between eMMC and SSDs in terms of sequential read and write speeds is substantial.
eMMC storage, while adequate for basic tasks, operates at transfer speeds around 400MB/s for the latest models.
In contrast, Solid State Drives, especially those utilizing NVMe protocols, can achieve speeds up to 7.0GB/s, making them exponentially faster than eMMC solutions.
This significant speed difference impacts everything from system boot times to file transfer rates and application load times.
Why Does Speed Matter?
Speed is not just about moving files quicker; it affects the overall responsiveness of your device.
For tasks that demand heavy read-and-write operations, such as video editing, gaming, and running advanced applications, SSDs offer the performance necessary to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
The faster your storage can read and write data, the less time you’ll spend waiting for tasks to complete, translating to increased productivity and a better user experience.
Storage Capacity: Room to Grow

Another critical factor in the eMMC vs. SSD discussion is storage capacity.
eMMC storage solutions are typically available in smaller sizes – often 32GB or 64GB, with some models offering up to 128GB or 256GB.
While suitable for devices where high storage capacity is not a priority, this limitation can be a significant drawback for users who need more space for their files, applications, and media.
On the other hand, SSDs start with capacities of around 128GB and can extend up to 2TB or more in consumer devices.
This vast range of storage options makes SSDs far more versatile, catering to the needs of both average users and professionals who require substantial storage for their projects and data.
Longevity and Durability
The topic of longevity and durability further distinguishes SSDs from eMMC storage.
SSDs are designed with durability in mind, featuring no moving parts and utilizing advanced technologies like wear leveling and garbage collection.
These mechanisms help distribute data evenly across the drive, minimizing wear on any given cell and extending the SSD’s lifespan.
In contrast, eMMC storage is more prone to wear and degradation over time, especially with intensive use.
Why Does Durability Matter?
Durability is crucial not only for the longevity of the storage medium itself but also for data integrity.
More durable storage solutions like SSDs are less likely to suffer from data corruption or loss due to physical impacts or wear and tear.
This makes SSDs a more reliable choice for users who value the safety and longevity of their data.
Balancing Budget and Performance

Cost is an unavoidable aspect of the decision-making process. eMMC storage, being more affordable, offers a cost-effective solution for manufacturers and, consequently, consumers.
This affordability makes eMMC a popular choice for entry-level devices, such as budget laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
However, the lower price point comes at the expense of performance and storage capacity.
SSDs, while more expensive, offer a significant improvement in performance and capacity.
The higher cost is justified by the benefits SSDs bring, especially for power users or those who prioritize speed and storage space.
As SSD technology continues to evolve, prices have been gradually decreasing, making SSDs more accessible to a wider audience.
Which is Better for You?
The answer to whether eMMC or SSD is better depends largely on your specific needs and budget.
If you’re looking for a cost-effective storage solution for light computing tasks, eMMC may be sufficient.
However, for those requiring higher performance, faster speeds, and larger storage capacities, SSDs are clearly the superior choice.
Considerations for Upgrading
For users contemplating an upgrade from eMMC to SSD, it’s essential to consider the compatibility and physical constraints of your device.
While upgrading can significantly improve performance and storage capacity, not all devices support such an upgrade due to eMMC being soldered onto the motherboard.
FAQs
Can eMMC be upgraded to SSD in tablets?
In most cases, no, because eMMC is soldered onto the device’s motherboard, making it difficult to replace or upgrade to a Solid State Drive.
Do SSDs use more power than eMMC storage?
Solid State Drives typically use more power than eMMC due to their higher performance capabilities, but the difference is minimal and often offset by SSDs’ efficiency and faster data processing.
Is data recovery easier on eMMC or SSD?
Data recovery can be more challenging on Solid State Drives due to their complex data management algorithms, such as TRIM and wear leveling, compared to eMMC storage.
Can I use both eMMC and SSD storage in one device?
Some devices may feature both eMMC and SSD storage, using eMMC for the operating system to reduce costs and a Solid State Drive for additional, faster storage.
Do SSDs improve battery life compared to eMMC?
Solid State Drives can improve battery life in devices due to their efficiency and faster data processing, which can reduce the time the drive needs to be active.
Are there any noise differences between eMMC and SSD storage?
Both eMMC and SSD storage are silent, as they are solid-state technologies without moving parts, unlike traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
Closing Thoughts
In the comparison of eMMC vs. SSD, Solid State Drive stands out as the superior storage solution in terms of performance, capacity, and durability.
While eMMC offers a cost-effective option for entry-level devices, SSDs provide the speed and space required for more demanding tasks and applications.
As technology progresses, the gap between these storage solutions continues to widen, with SSDs leading the way in innovation and performance.